Stress fractures are a common injury that affects runners and triathletes. They occur when the bones in the feet, legs, or hips become overloaded from repetitive stress during exercise. Stress fractures can be incredibly painful and debilitating if left untreated and can cause long-term complications if not dealt with appropriately.
What Are Stress Fractures?
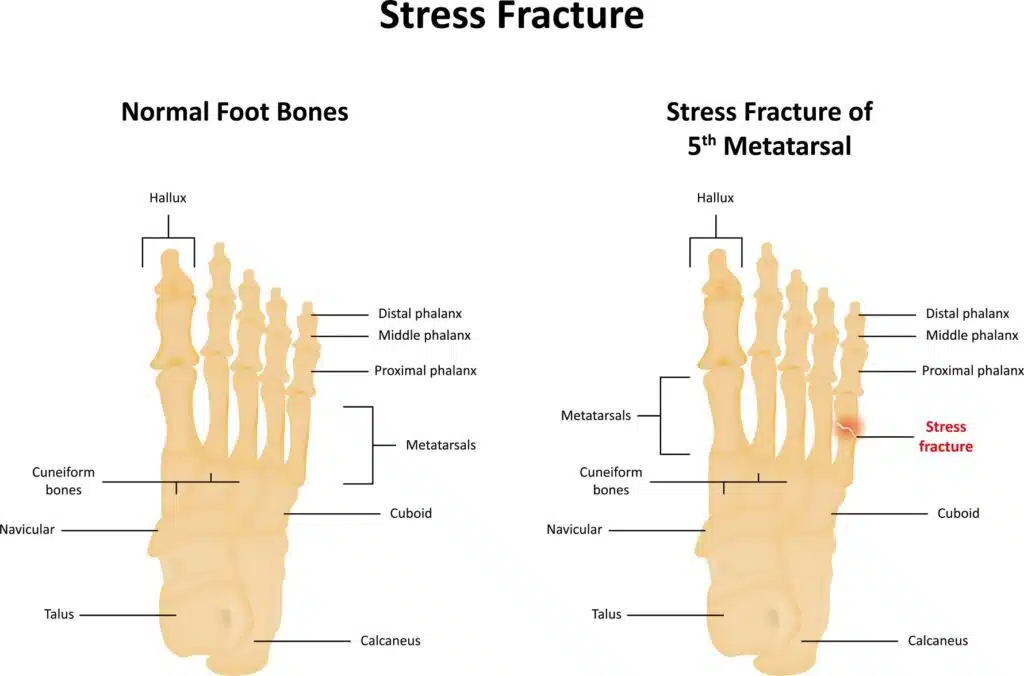
Stress fractures are overuse injuries caused when stress on the bones is greater than the body’s ability to repair them. They typically occur in weight-bearing bones such as the tibia, fibula, and metatarsals of the feet, or bones of the legs and hips.
Common Causes Of Stress Fractures
Stress fractures usually result from repetitive stress or stress overload that the bones can’t recover from quickly enough. This stress often comes from running or other exercises involving regular, repetitive impact on the feet and lower legs.
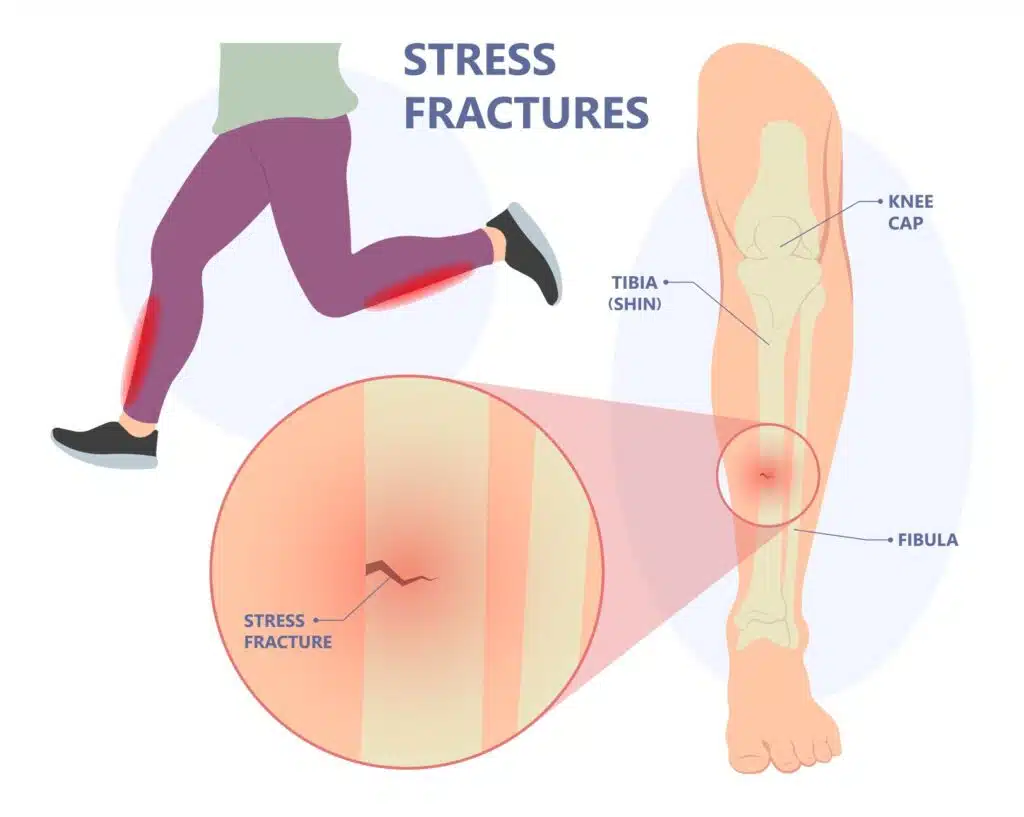
Common Symptoms Of Stress Fractures
The primary symptom of a stress fracture is pain in the area affected, which may worsen with activity and lessen with rest. Swelling, bruising, and tenderness may also occur. In some cases, stress fractures can be difficult to diagnose because the pain is similar to muscle soreness or shin splints.
Stress Fractures vs Shin Splints
Stress fractures are caused by overstressing bones that can’t repair themselves quickly enough, while shin splints are usually the result of inflammation and microdamage to the tibia bone and muscles surrounding the tibia. Symptoms of stress fractures include pain that worsens with activity and lessens with rest, swelling, bruising, tenderness at the stress fracture site, and difficulty walking or running without pain. Symptoms for shin splints include burning or aching pain in the lower leg along the shinbone, tenderness to touch along the inner border of the shinbone, tight calf muscles, and mild swelling in the lower leg. Treatment for stress fractures includes rest from activities that aggravate symptoms, icing the area to reduce swelling, and using crutches to keep weight off the affected limb. Treatment for shin splints includes ice therapy combined with stretching exercises to reduce inflammation and relieve pain, the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen sodium to reduce swelling and pain, massaging the affected area after exercise, and wearing supportive shoes during sports activities.
Diagnosing Stress Fractures
Stress fractures can be tricky to diagnose since the pain may be similar to other conditions such as shin splints. To diagnose stress fractures, your healthcare provider (including chiropractic physicians specially trained in Sports Medicine) will likely perform a physical exam and ask you questions about your symptoms and activity level. Your doctor may also order imaging tests, such as an MRI or a CT scan, to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Stress Fracture Recovery
The main treatment for stress fractures is rest from activities that aggravate the symptoms, as well as icing the area to reduce swelling and using crutches to keep weight off the affected limb. Your doctor may also suggest taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen sodium, to reduce swelling and pain. Depending on the severity of the stress fracture, your doctor may also suggest further treatment like physical therapy or rehab and treatments with a sports medicine chiropractor for further stress fracture recovery.
When you have a stress fracture, it is important to rest. I mean actually rest. This is one of the few reasons that I will be adamant about rest as most runners that I treat are able to continue running and still recover from their problem.
You can also put ice on the area that hurts and use crutches to keep weight off of the limb with the stress fracture. Taking medicine like ibuprofen or naproxen sodium may help reduce swelling and pain. Treatments like cold laser therapy can speed recovery time.
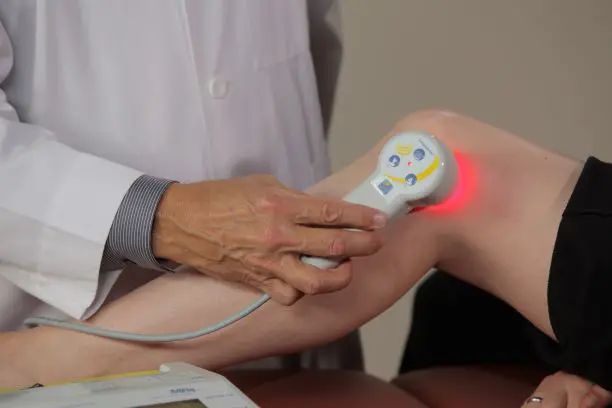
It is important to remember that stress fractures can take 6-8 weeks–or longer–to heal, so it is important to be patient with the healing process. Listen to your body and take the time you need to heal properly. Doing too much too soon could re-injure yourself or delay recovery. After stress fracture recovery is complete, it’s important to slowly reintroduce activities and strengthen the area with stretching and low-impact strengthening exercises. This will help reduce stress on the bones and make them stronger so they can handle stress better in the future.
If you think you may have a stress fracture, contact your doctor right away for diagnosis and treatment options. With rest, proper treatment, and stress fracture recovery, you can get back to your pre-injury activities.
How can Nutrition Affect Stress Fractures?
Nutrition can have a direct effect on stress fracture recovery and prevention. Since stress fractures are caused by overuse or lack of nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and minerals that help build strong bones, it is important to make sure you are getting enough of these essential vitamins and minerals in your diet. Eating foods that contain calcium like milk, leafy greens, and salmon can help strengthen bones and make them less prone to stress fractures. Additionally, avoiding certain substances, like caffeine, alcohol, and cigarettes, can decrease stress fracture risk by decreasing inflammation in the body.

Tips on Preventing Stress Fractures
1. Strengthen Bones: Eating foods that are rich in calcium, such as milk, leafy greens, and salmon, can help strengthen bones and make them less prone to stress fractures.
2. Wear Appropriate Shoes: Wearing the right shoes for your activity level is immensely important when it comes to stress fracture prevention. Make sure you have proper arch support and cushioning in your shoes to absorb shock when running or playing sports.
3. Avoid Excessive Exercise: Increasing exercise too quickly or pushing yourself beyond your limits can cause stress fractures due to overuse of muscles or bones in the body; try starting a new exercise routine slowly and increase difficulty gradually over time instead of all at once.
4. Keep Bones Strong with Vitamins/Minerals: Getting plenty of essential vitamins like Vitamin D, Calcium, Magnesium, Zinc, Potassium, and Iron will help keep bones strong enough to handle stress much better than weak ones will be able to do so.
5. Don’t Smoke/Drink Too Much Alcohol/Caffeine: Smoking cigarettes or drinking excessive amounts of alcohol can decrease stress fracture resistance by increasing inflammation throughout the body; caffeine may also reduce healing speed if consumed excessively which can prolong stress fracture recovery.
By taking the right steps and following your doctor’s orders during stress fracture recovery, you can get back to your pre-injury activities in no time. Remember to strengthen bones with vitamin and mineral-rich foods, wear appropriate shoes for activity levels, avoid excessive exercising, and don’t overdo substances like alcohol or caffeine
What Makes a Stress Fracture Worse?
Activities that put too much stress on the limb with a stress fracture can make it worse. Examples of activities to avoid include running, jumping, and any other high-impact exercise. Also, not allowing enough time for proper stress fracture recovery can cause a stress fracture to become worse. Not following your doctor’s advice when it comes to rest and nutrition can also contribute to making the stress fracture worse. Finally, wearing improper footwear or using incorrect form during sports activities may increase the chances of aggravating an existing stress fracture.
Conclusion
Stress fractures can be painful and frustrating, but with the right knowledge and preventative measures stress fracture recovery is possible. Resting from activities that aggravate symptoms, icing the area to reduce swelling, taking NSAIDs for pain relief, and physical therapy are all effective stress fracture treatment options. Additionally, incorporating bone-strengthening nutrients into your diet such as calcium, vitamin D, and minerals can help prevent stress fractures in the future. It’s also important to avoid substances like caffeine or alcohol which increase inflammation in the body. With proper care and attention, stress fractures can be managed without disrupting running or training routines too much! If you think you may have a stress fracture, it’s best to contact your healthcare provider immediately so they can diagnose and treat it properly before any further damage occurs.
