Sacroiliac joint dysfunction (SIJD) is a common source of lower back pain, which is incredibly common among adults. As many as 90% of people will experience low back pain at some point in their lives and up to 30% are thought to be dealing with SI joint issues. Sacroiliac joint pain can affect anyone regardless of lifestyle or demographic characteristics such as gender and race but those who lead a sedentary life or struggle with obesity may be more likely than the general population to encounter related problems. While it is common, sacroiliac joint dysfunction is often overlooked by physicians.
What is the Sacroiliac Joint?
The sacroiliac joint (SIJ) is located in the lower back, just below the belt line and slightly to one side of center. If you have ever seen a person with two dimples on their lower back that are offset from the center, you will know where the top part of the SI joint is located. The SI joint is a mechanical link that connects the sacrum, which forms the base of the spine, to the pelvis. It consists of two surfaces, one on each side of the sacrum, that are held together by a series of ligaments and muscles. The sacroiliac joint is an irregularly shaped, synovial and fibrocartilaginous joint that allows minimal motion—about 4 degrees of rotation and up to 1.6 mm of translation. This is an extremely small amount of motion, but it can have a major impact on one’s daily activities, especially if it is not functioning properly. Walking is one of the main activities that stresses the SI joint.
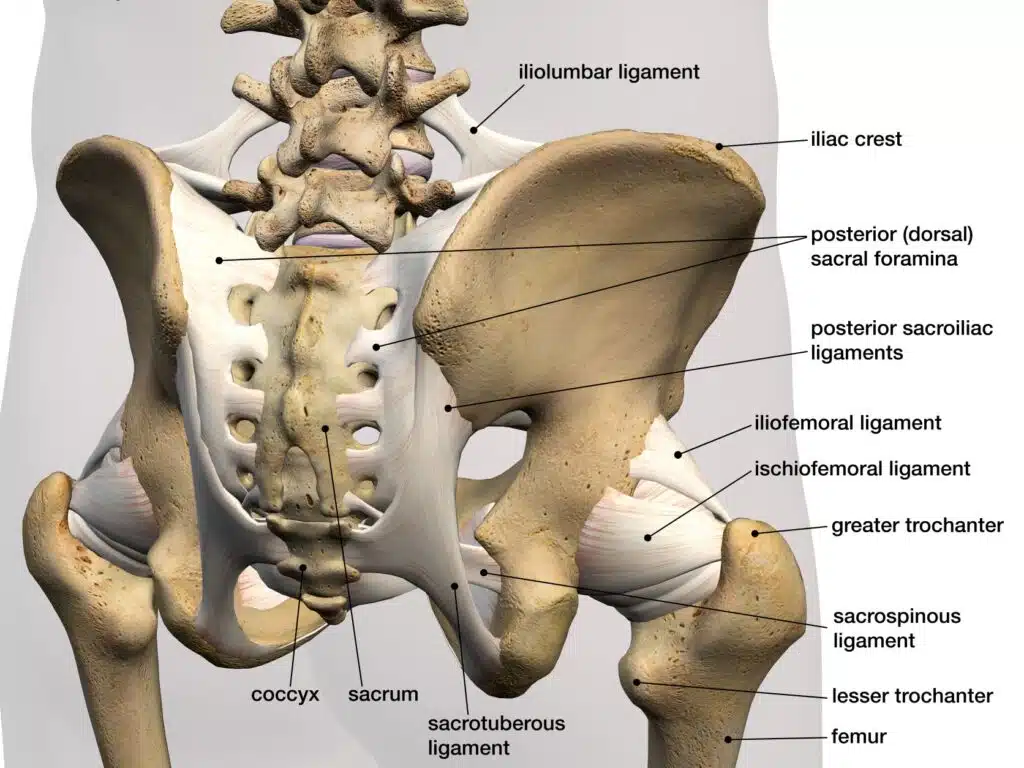
Causes of SI Joint Dysfunction
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction can arise from many different sources which disrupt the sacroiliac’s normal mechanics including leg length inequalities, gait abnormalities and lower extremity joint pain. Pregnancy is also a common trigger due to weight gain, gait changes and postural stress.
Anatomical variations in the sacroiliac like an accessory joint may also be associated with increased risk for SIJD degeneration over time if left untreated. Finally, “arthritic” SIJD results from either osteoarthritis or inflammatory arthropathies that produce sacroiliitis and resulting pain—often beginning as morning discomfort lasting more than half an hour before dissipating after exercise begins.
Injuries to the sacroiliac joint can be caused by a variety of etiologies, with 88% coming from either repetitive microtrauma or acute trauma. While it is very common among sedentary people, a high prevalence among athletes is seen in these cases. Around 20% of cases result due to pregnancy-related hormone changes that relax ligaments leading to hypermobility within the joints while 4 % remain as idiopathic issues without any determined cause other than pain and abnormality on X-rays. As people age past their fifth decade, fusion between SI joints becomes more common.
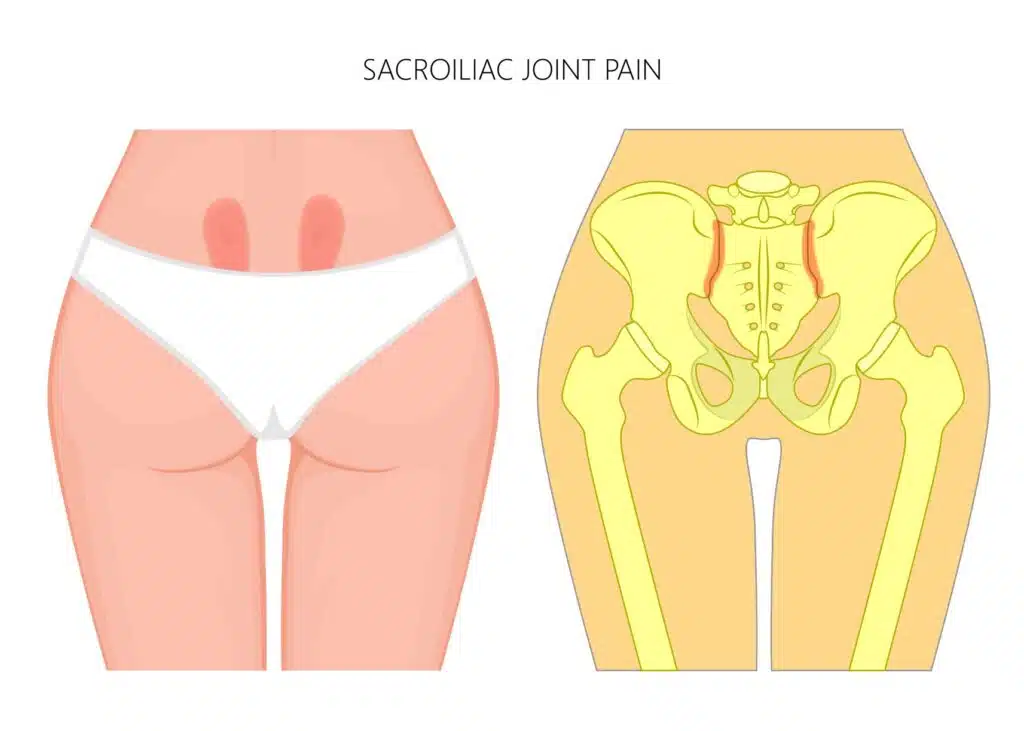
Symptoms of Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction
Sacroiliac joint syndrome is often a tricky condition to diagnose, as its symptoms can be confused with other types of low back pain. However, SI joint dysfunction has the tendency to cause characteristic symptoms, including localized buttock-area discomfort and sharp shooting pains down the posterior thigh that usually do not extend past the knee. The pain is often just below the beltline, slightly to one side of center. Pain often worsens when standing on the affected side and improves with lying down. Additionally, difficulty sitting for extended periods due to pain may occur along with tenderness near where the back dimples would be.
It is common to have increased pain when standing up from a sitting position. Climbing stairs can be difficult due to pain. Pain can occur while bending forward while seated, and lessen when lying down. Pain from SI joint dysfunction can be severe and crippling making walking impossible. If left untreated sacroiliac joint problems can become worse over time creating a self-perpetuating cycle of discomfort.
Many people with sacroiliac joint dysfunction commonly think they have sciatica because pain can radiate down into the posterior thigh, but a careful history and exam show this is not the case. Unfortunately because of this, SI joint dysfunction is commonly misdiagnosed as sciatica by healthcare providers as well.
Treatment Options for SI Joint
Effective treatment for SI joint dysfunction involves a conservative approach such as manipulation, exercise, and specialized interventions. Examples include manual therapy to restore motion in hypomobile joints, support belts or orthotics, mobilization techniques, cold laser therapy, kinesio taping, ice packs and e-stim applications which can help alleviate pain and inflammation.
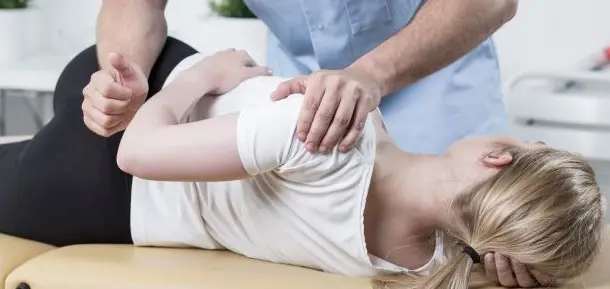
Manipulation of the SI joint is one of the most effective treatments for sacroiliac joint dysfunction. Manipulation can be done like a traditional chiropractic adjustment or a gentler & less forceful adjustment can be used. The goal is to get the best outcome for the patient that is best tolerated. In some cases, mobilization of the joint is what is needed. In my experience, manipulation of SI joint dysfunction can result in some of the most dramatic recoveries of patients who can barely move.
To effectively address Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction symptoms, clinicians may utilize a variety of other techniques including Graston Technique and/or cupping therapy. These treatments can be used on the Long Dorsal Sacroiliac Ligament for improved flexibility alongside targeted stretching of specific muscles like gluteus, hamstrings, piriformis and latissimus dorsi. Lastly, strengthening various structural parts that support lumbopelvic stability such as transverse abdominus muscle groups or hip adductors is essential in assisting recovery from this dysfunction.

To help manage SIJ pain, patients should be mindful of their posture and ergonomics. Certain activities such as standing on the affected leg for long periods or sitting in one spot can exacerbate symptoms; however, arch supports, orthotics or a heel lift may address any structural issues while sacroiliac support belts could also reduce discomfort associated with joint instability. Glucosamine and chondroitin have demonstrated some benefit for those suffering from osteoarthritis but there is not yet sufficient evidence to suggest PRP injections are effective against SIJ pain specifically.
Patients who have not responded to traditional conservative treatments for sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain may require consultation regarding SIJ injections, radiofrequency neurotomy or even surgical intervention and fusion. In some cases, a corticosteroid injection or anesthetic can help relieve symptoms while more advanced interventions such as radiofrequency ablation and rhizotomy can also provide lasting relief when deemed necessary.
Prevention tips for sI joint dysfunction
- Maintain a healthy weight as excess weight increases the stress on your joints
- Perform regular stretching exercises to increase flexibility and reduce stiffness in your sacroiliac joint
- Strengthen the muscles surrounding your sacroiliac joint with core-strengthening exercises like Pilates
- Avoid sudden, jerking movements that can cause injury to this area of the body
- Wear supportive shoes with good arch support
- Get adequate rest between activities and throughout the day
- Don’t sit for long periods of time; opt instead for standing or walking regularly
- Utilize proper body mechanics when lifting heavy objects or engaging in physical activity
- Practice yoga poses designed specifically for sacroiliac joint health
- Make sure you have comfortable posture while sitting or standing
Conclusion
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction can be a difficult and painful condition to manage, but with the right combination of preventive measures and treatments such as physical therapy, orthotics, mobilization techniques, ice packs and e-stim applications you may find relief. If sacroiliac joint pain persists despite these conservative approaches, it is important to seek out a healthcare provider like a sports medicine chiropractor who will have specialized knowledge in treating SI joint issues. With their help, you could reduce your symptoms or even avoid surgery altogether. Don’t hesitate if you are experiencing sacroiliac joint pain – finding the appropriate medical professional now could make all the difference later!
