Knee osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disorder that occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions and lubricates the bones of the knee joint becomes worn down. It is one of the most common forms of arthritis, estimated to affect up to 10% of men and 13% of women in the United States. Knee osteoarthritis can cause pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced range of motion in the knee joint.
Symptoms of Knee Osteoarthritis
Knee osteoarthritis may cause several symptoms, with the most common being pain and stiffness in the knee joint. This pain usually starts gradually and can become worse when engaging in physical activities or exercise. Over time, the knee may become swollen or tender to the touch, and the range of motion in the affected area can begin to decrease. Knee osteoarthritis may also cause a cracking or popping sound when the knee joint moves, and decreased ability to perform everyday tasks such as walking, climbing stairs, and kneeling.
Causes And Risk Factors
Knee osteoarthritis is typically caused by wear and tear on the knee joint. Knee osteoarthritis can be a result of aging, injury to the knee, being overweight or obese, previous surgery on the knee joint, and certain genetic conditions. Knee osteoarthritis is more common in people aged 45 and older, as well as those who have had previous injuries to their knees or suffered from conditions such as gout. Knee osteoarthritis can also be caused by overuse of the joint, such as engaging in repetitive activities that put strain on the knee.
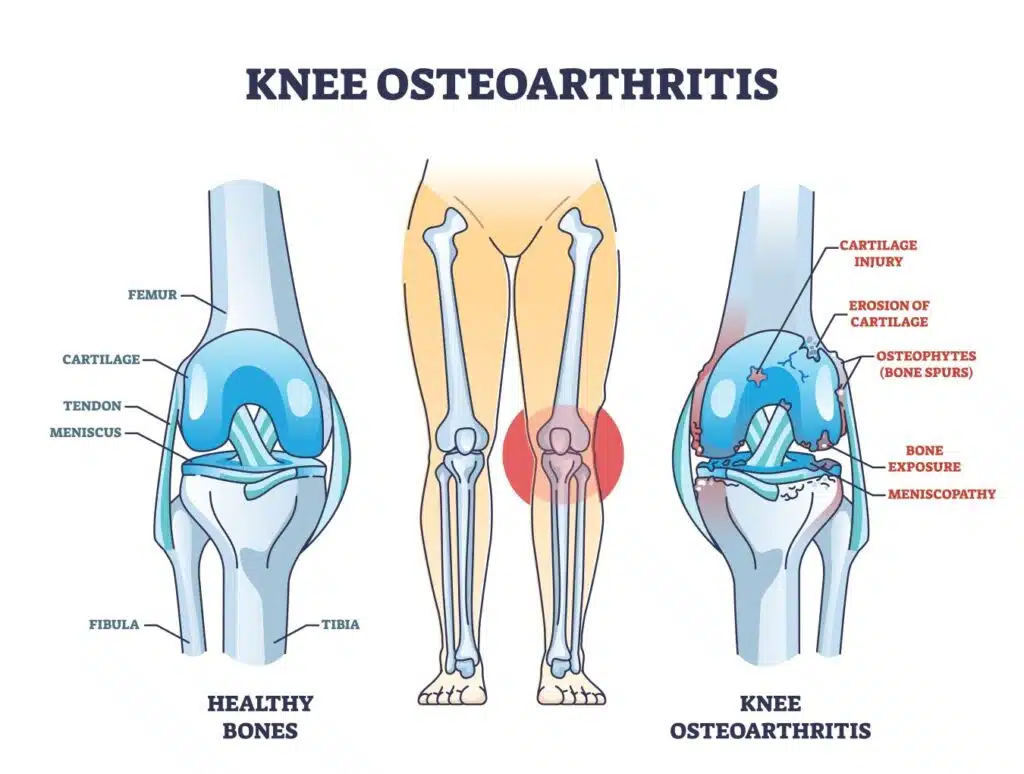
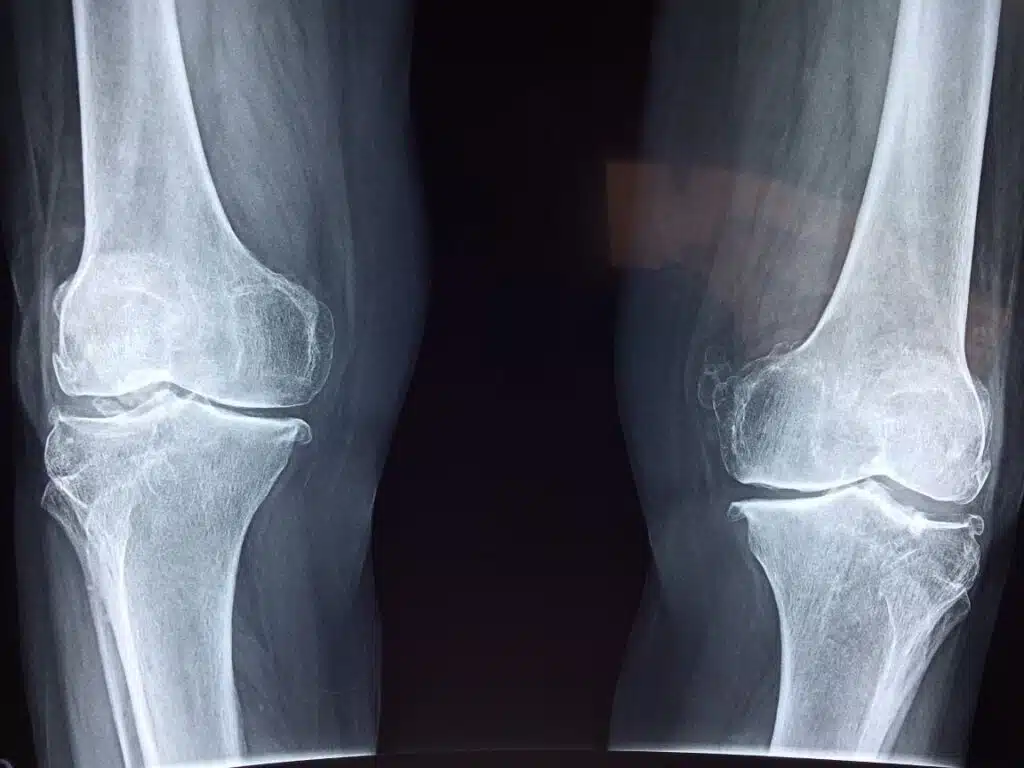
Diagnosis of Knee Osteoarthritis
Knee osteoarthritis is typically diagnosed through a physical examination and imaging tests such as x-rays or MRI scans.
Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis
Knee osteoarthritis is typically treated with a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication, physical medicine and possibly surgery. Lifestyle changes can include weight loss (if necessary), low-impact activities that do not aggravate the knee joint (such as swimming or biking), and using supportive devices such as canes or braces. Medications, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help to reduce pain and inflammation. Corrective exercises can help to improve range of motion and strength in the knee joint.
Chiropractic manipulative therapy is an effective treatment option for knee osteoarthritis. This form of manual therapy involves using specific techniques to manipulate and realign the joints to reduce pain and improve range of motion. With chiropractic adjustments, patients may experience improved mobility, reduced pain levels, and enhanced quality of life.
Graston Technique is a form of manual therapy used to treat knee osteoarthritis and other joint-related conditions. It involves using specialized stainless-steel instruments to detect and treat areas of the body where muscle, tendon, or ligament pain has accumulated due to injury or overuse. The instruments are used to break down scar tissue and promote healing in the affected areas. Graston Technique can be used to reduce pain, improve range of motion, and increase flexibility in the joint. Graston Technique is typically combined with other therapeutic interventions such as corrective exercises and stretching to achieve optimal results.
Cold laser therapy is a relatively new form of treatment for knee osteoarthritis that uses low-level lasers to reduce inflammation and pain. The cold laser helps stimulate the body’s natural healing process by increasing blood flow, reducing swelling, and promoting cell regeneration. It can be used in conjunction with other treatments to provide relief from pain and disability. Additionally, cold laser therapy is non-invasive, safe, and free of side effects making it an attractive option for many patients seeking relief from this condition.
Kinesiotaping uses special elastic tape that is applied in specific patterns to provide support and promote healing of the affected joints. It helps reduce pain, improve range of motion, and increase blood flow to the knee joint. Kinesio taping also provides stability and encourages proper alignment of the joint during activity, helping to reduce the risk of further injury. Kinesiotaping is safe and non-invasive, making it a popular choice for many knee osteoarthritis patients.
When conservative treatments are not effective in relieving symptoms, certain forms of regenerative medicine can be helpful. Recent advances in stem cell research have presented promising potential for treating knee osteoarthritis. Stem cells can be used to replace damaged tissues and restore function to the affected joint, providing relief from pain and disability associated with this condition. With further clinical trials, stem cell-based therapies may become an important part of managing knee osteoarthritis in the future.
In addition to stem cell treatments, other forms of regenerative medicine such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and extracellular matrix (ECM) therapies are also being explored for their potential benefits in treating knee osteoarthritis. PRP is a concentrate of platelets derived from the patient’s blood, which can be used to stimulate healing and provide relief from pain. ECM is an injectable gel-like substance made up of the extracellular matrix components found in healthy cartilage, which may help regenerate damaged tissue and reduce joint inflammation. Patients should discuss their options with a medical professional to determine which therapies are most suitable for their condition.
Surgery may be necessary if the knee osteoarthritis is severe, with options such as arthroscopic surgery or total knee replacement available.
What Home Treatments are available?
Home treatments for Knee Osteoarthritis include dietary changes, supplements and yoga. Dietary modifications may include avoiding inflammatory foods, increasing intake of anti-inflammatory foods such as omega-3 fatty acids or probiotics, or using herbs such as ginger and turmeric to reduce pain and inflammation. Supplements including glucosamine sulfate and chondroitin sulfate may also be beneficial in treating Knee Osteoarthritis symptoms. Finally, yoga practice can help increase flexibility and range of motion in the affected knee joint. Ultimately a combination of these treatments should be discussed with a health practitioner before starting any new regime.
Additionally, people with knee osteoarthritis should avoid activities that put strain on the knee joint such as running, jumping, climbing or descending from ladders or stairs, and kneeling. These activities can make pain worse. Instead, seek out low-impact forms of exercise such as swimming, biking, or walking. Lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy weight and exercising can help to lessen the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis.
Conclusion
Overall, there are many treatment options available for knee osteoarthritis. Each patient should discuss their symptoms and options with a medical professional to determine the best course of action for their condition. With proper care and management, many patients experience reduced pain levels, improved range of motion, and enhanced quality of life.
The most important thing to remember is that knee osteoarthritis is manageable and there are treatments available that can help reduce pain and improve quality of life. It is important to discuss your symptoms with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action for you.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can exercise help with Knee Osteoarthritis pain relief?
Exercise is an important part of relieving knee osteoarthritis pain and increasing mobility. Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, biking, and Tai Chi are all beneficial for knee osteoarthritis sufferers. These activities help strengthen the muscles around the knee joint, providing support and stability while also improving range of motion. It is important to speak with your doctor or physical therapist about which exercises will be most beneficial for you. Additionally, patients should avoid activities that put strain on the knee joint such as running, jumping, climbing or descending from ladders or stairs, and kneeling. These activities can make your pain worse.
Ultimately, knee osteoarthritis is a manageable condition and there are treatments available to help reduce pain and improve quality of life. It is important to speak with your healthcare provider about which treatment options will be best for you. With the right combination of lifestyle changes, medications, physical or occupational
Does diet have an impact on Knee Osteoarthritis?
Yes, diet can have an impact on knee osteoarthritis symptoms. Eating a balanced diet filled with fresh fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, nuts and seeds can help reduce inflammation in the joints and improve overall health. Additionally, eliminating certain inflammatory foods such as processed meats, refined sugars, fried foods and trans fats can help reduce knee osteoarthritis pain. Increasing the intake of anti-inflammatory foods such as omega-3 fatty acids or probiotics, or using herbs such as ginger and turmeric to reduce pain and inflammation can also be beneficial in treating symptoms. Ultimately a combination of dietary changes should be discussed with a health practitioner before starting any new regime.
An anti-inflammatory diet is a way of eating that focuses on incorporating foods with anti-inflammatory properties into your meals. Anti-inflammatory diets are based on the idea that certain foods can reduce inflammation and provide health benefits, while other pro-inflammatory foods can increase inflammation in the body. Examples of pro-inflammatory foods include processed meats, refined sugars, fried food and trans fats, while examples of anti-inflammatory foods include fresh fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains nuts and seeds. Eating an anti-inflammatory diet can help to reduce inflammation in the joints as well as improve overall health. It is important to speak with your healthcare provider about the best dietary approach for Knee Osteoarthritis.
Are there any lifestyle changes that can lessen the symptoms?
Yes, many lifestyle changes can lessen the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis. One of the most important changes is engaging in regular low-impact exercise. Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, biking, and Tai Chi can help strengthen the muscles around the knee joint, providing support and stability while also improving range of motion. Additionally, knee osteoarthritis patients should avoid activities that put strain on the knee joint such as running, jumping, climbing or descending from ladders or stairs, and kneeling, as these activities can make your pain worse.
Other lifestyle changes to lessen knee osteoarthritis symptoms include following a balanced diet free of inflammatory foods such as processed meats, refined sugars, fried foods and trans fats. Additionally, knee osteoarthritis sufferers should aim to maintain an ideal body weight and use heat or cold therapy to reduce swelling and inflammation. Finally, targeted stretching exercises from yoga practice can help increase flexibility and range of motion.
It is important to speak with your healthcare provider about which lifestyle changes will be most beneficial for you and your knee osteoarthritis symptoms.
What medications are available to treat Knee Osteoarthritis?
There are several different types of medications that can be used to treat knee osteoarthritis, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologic therapies. NSAIDs are the most commonly prescribed medications for Knee Osteoarthritis and they can help reduce inflammation and pain. Corticosteroids are a stronger form of anti-inflammatory medication that can be injected directly into the joint to help reduce Knee Osteoarthritis symptoms. DMARDs are used for more severe cases and they can help slow the progression by targeting specific proteins that cause inflammation. Finally, biologic therapies are newer medications used to treat Knee Osteoarthritis and they work by targeting the body’s immune system to reduce inflammation. It is important to speak with your healthcare provider about which medication will be best for you.
