Hip osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that affects the hip joints, causing pain and disability. It is one of the most common forms of arthritis and has been estimated to affect around 10 million people in the United States alone. Hip osteoarthritis can occur at any age, but it is more common among older adults, with an overall prevalence rate of 3-4% in individuals over 65 years old. The incidence of hip osteoarthritis increases with age, affecting up to 33% of those aged 85 or above. Hip osteoarthritis can have a significant impact on the quality of life for sufferers due to its painful symptoms and reduction in mobility; thus, it is important to understand its causes, diagnosis, treatments and prevention strategies.
What is Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is a joint disorder that occurs when the protective cartilage between bones gradually wears away. This leaves the bones in contact with each other, often leading to pain, swelling and reduced mobility in the affected joint. It is caused by long-term wear and tear of the joint, usually due to aging or previous injury. Hip osteoarthritis specifically occurs in the hip joint, which is a ball-and-socket joint composed of the top of the thighbone (femur) and the acetabulum, or socket, which is located on the pelvis.
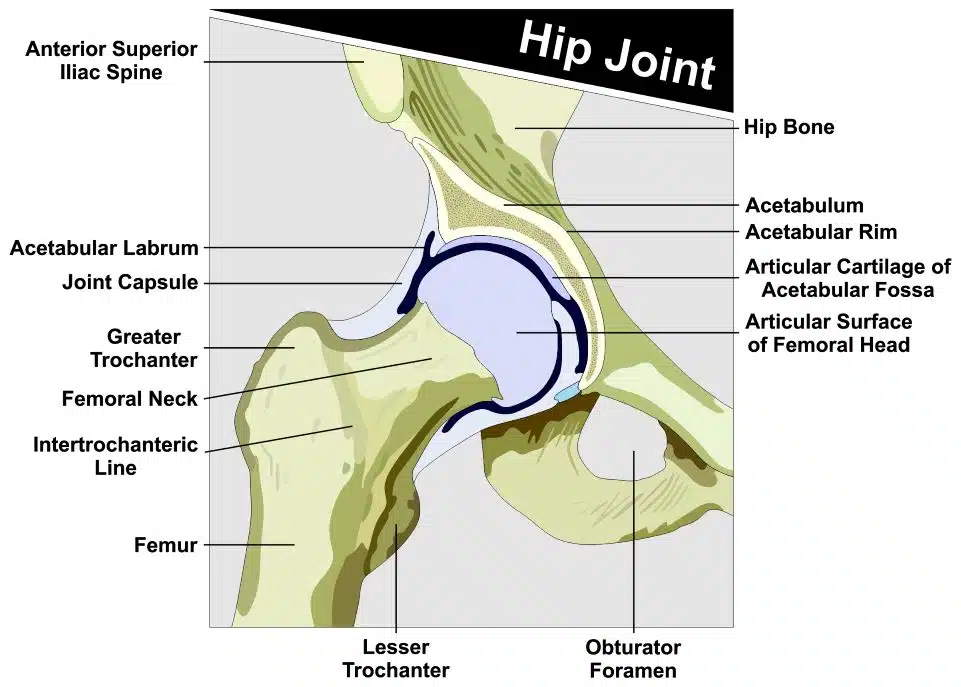
Symptoms of Hip Osteoarthritis
One of the most common signs of hip osteoarthritis is aching pain in the groin, buttock or thigh that worsens with activity. Other symptoms may include stiffness and difficulty with everyday activities such as walking up stairs, getting up from a chair or climbing into a car. Hip osteoarthritis can also cause clicking and grinding.
What Causes Hip Osteoarthritis?
Hip osteoarthritis is caused by long-term wear and tear of the joint, usually due to aging or previous injury. Age-related changes such as decreased cartilage production and increased bone formation can also contribute to hip osteoarthritis. Genetics may play a role in some cases, with people who have certain genetic variants being more likely to develop hip osteoarthritis than others. Additionally, obesity has been linked to an increased risk; this could be because extra weight puts added strain on the joints, leading to accelerated wear and tear over time. Finally, lifestyle factors such as smoking and lack of exercise may also increase the risk of developing hip osteoarthritis due to their effects on inflammation levels within the body.
Unfortunately, NSAIDs have been shown to damage cartilage cells leading to more rapid onset or progression of arthritis when used consistently over a long period of time. Cortisone is also known to cause damage to joints with frequent administration, which is why one should get more than about 3 shots in a joint in a year.
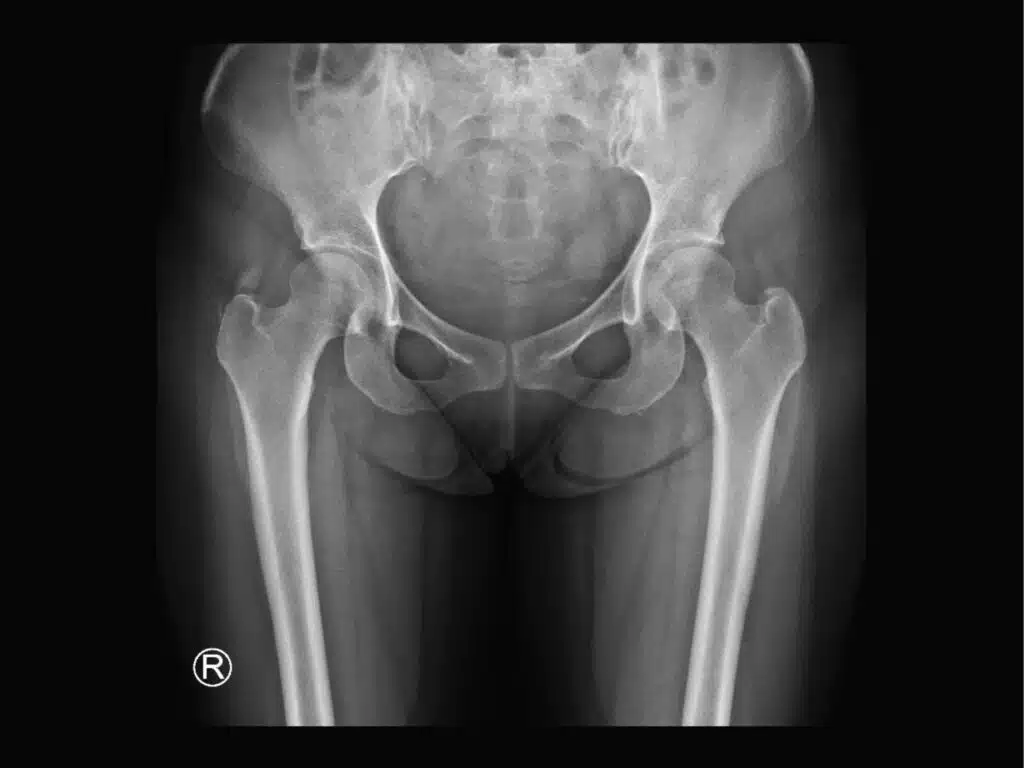
The exact cause of hip osteoarthritis is still unclear, but a combination of factors including age, genetics, injury and lifestyle are thought to play a role. Hip osteoarthritis can be difficult to diagnose as the symptoms are often similar to those of other conditions; thus physical examination and imaging tests such as X-rays and MRI scans may be necessary to make
Diagnosis
Hip osteoarthritis can be difficult to diagnose as the symptoms are often similar to those of other conditions. A physical examination and imaging tests such as X-rays and MRI scans can help to make a definitive diagnosis. Additionally, blood tests may also be used to measure levels
The exact cause of hip osteoarthritis is still unclear, but a combination of factors including age, genetics, injury and lifestyle are thought to play a role. Hip osteoarthritis can be difficult to diagnose as the symptoms are often similar to those of other conditions; thus physical examination and imaging tests such as X-rays and MRI scans would most likely be used to make a definitive diagnosis.
Treatment of Hip Osteoarthritis
The goal of treatment for hip osteoarthritis is to reduce pain and improve mobility. Treatment options may include medications, lifestyle changes (such as exercise) and physical therapy. In some cases, surgery may be necessary. Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids may be used to reduce pain and inflammation in the joint.
Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in low-impact exercise, using supportive devices (such as a cane or walker) and avoiding straining activities can also help to reduce the symptoms of hip osteoarthritis. corrective exercises may also be used to strengthen the muscles around the joint and improve mobility.
In cases where conservative treatments are not effective, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace the affected joint. Hip replacement is one of the most common surgeries for osteoarthritis, although it is usually only considered in cases where other treatments have been unsuccessful. Hip resurfacing may be an option for younger or more active patients.
Chiropractic adjustments of the hip can be an effective treatment for hip osteoarthritis and can help to reduce pain and improve mobility. Through special techniques and adjustments, a chiropractor can adjust the hip joint and soft tissues to alleviate pain and promote healing. This approach involves targeted manipulation of the affected areas that helps to reduce inflammation, improve alignment and mobility, and promote healing.
Massage therapy of the hip can be an effective treatment, helping to reduce pain and improve mobility. Massage therapy works by helping to improve circulation and increase the range of motion in the hips. This helps to reduce inflammation and stiffness, thereby decreasing pain levels. Additionally, massage therapy of the hip joint helps to release tension in the muscles, which can further reduce pain and promote healing.
Graston Technique can be an effective treatment for hip osteoarthritis. Graston Technique is a type of instrument-assisted soft tissue mobilization that can help to reduce pain and improve mobility in the hip joint. The technique utilizes specially designed stainless-steel instruments to locate and target areas of muscle spasm, inflammation, adhesions and scar tissue. This helps to release tension, break up adhesions and reduce pain levels.
Cold laser therapy can also help reduce pain associated with hip arthritis.
Tips for Living with Hip Osteoarthritis
Living with hip osteoarthritis can be challenging and painful, but it does not always have to be. Many people have no pain despite having degeneration.
There are several tips that can help you manage the pain and discomfort associated with hip osteoarthritis. These tips include maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, using supportive devices such as a cane or walker, avoiding straining activities, engaging in low-impact exercise, getting regular chiropractic manipulation of the hip joint, receiving massage therapy for the hip joint and utilizing Graston Technique to the hip for reducing pain levels. By following these tips, you will be able to reduce your hip osteoarthritis symptoms so that you can live comfortably and enjoy life again.
